The impact of interest rates on the economy is a topic of great significance and relevance to individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Interest rates play a pivotal role in shaping the overall financial landscape, influencing borrowing costs, investment decisions, and consumer spending. Understanding the dynamics of interest rates and their effects on the economy is crucial for making informed financial decisions and for predicting economic trends.
One of the primary ways in which interest rates impact the economy is through their influence on borrowing costs. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes more attractive as individuals and businesses can access capital at a lower cost. This, in turn, fosters increased investment in various sectors of the economy, such as housing, business expansion, and infrastructure development. Conversely, when interest rates rise, borrowing costs increase, leading to a decrease in borrowing activity and a potential slowdown in economic growth. By examining the impact of interest rates on borrowing costs, we can gain insights into the mechanisms through which interest rates shape the overall economic landscape.
The Relationship Between Interest Rates and Economic Growth
Interest rates play a crucial role in shaping the overall economic growth of a country. The relationship between interest rates and economic growth is a complex one, and understanding this connection is essential for policymakers, investors, and individuals alike. In this article, we will explore the impact of interest rates on the economy and delve into the factors that influence this relationship.
1. Effect on Borrowing and Investment
One of the primary channels through which interest rates impact economic growth is the effect on borrowing and investment. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes more attractive, as the cost of capital is reduced. This, in turn, stimulates investment and business expansion, leading to increased economic activity and growth. On the other hand, high interest rates can discourage borrowing and investment, limiting economic growth.
2. Influence on Consumer Spending
Interest rates also have a significant impact on consumer spending, which is a vital component of economic growth. When interest rates are low, consumers are more likely to borrow for large purchases such as homes and cars. This increased spending boosts aggregate demand, leading to economic expansion. Conversely, high interest rates can discourage consumer borrowing, resulting in reduced spending and potential economic slowdown.
3. Effects on Exchange Rates and Trade
Interest rates can affect exchange rates, which, in turn, impact a country’s trading relationships. When a country’s interest rates are higher than those of its trading partners, its currency tends to appreciate. This makes exports more expensive and imports cheaper, potentially leading to a decline in trade and economic growth. On the other hand, lower interest rates can lead to a depreciation of the currency, making exports more competitive and stimulating economic growth through increased trade.
4. Influence on Saving and Investment Decisions
The level of interest rates can also influence saving and investment decisions by individuals and households. Higher interest rates can incentivize saving, as individuals can earn more from their savings. However, this may result in reduced consumer spending and potential dampening of economic growth. Conversely, lower interest rates can discourage saving in favor of spending and investment, boosting economic activity.
In conclusion, the relationship between interest rates and economic growth is a dynamic and intricate one. Interest rates impact borrowing, investment, consumer spending, exchange rates, trade, and saving decisions, all of which play a crucial role in shaping the overall economic growth of a country. Recognizing and understanding this relationship is vital for policymakers and individuals alike, as it aids in making informed decisions that can enhance economic prosperity.
The Effects of Increasing or Decreasing Interest Rates on Investment and Consumption
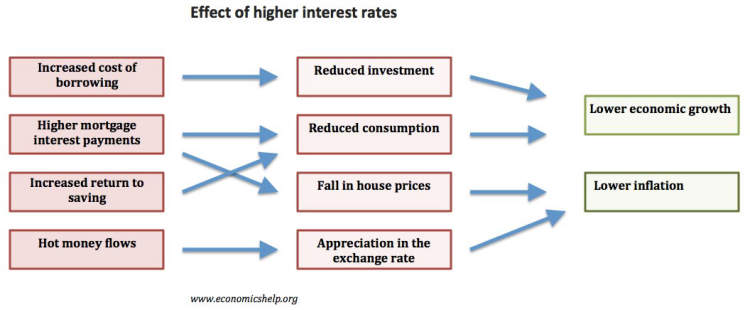
Interest rates play a crucial role in determining the levels of investment and consumption in an economy. When interest rates fluctuate, they have significant implications for businesses, individuals, and the overall economic growth.
1. Impact on Investment
When interest rates increase, the cost of borrowing goes up, making it more expensive for businesses to take out loans to finance investments. This leads to a decrease in investment as companies become more cautious about taking on additional debt. Higher interest rates also make other investment options, such as bonds, more attractive compared to riskier ventures. Consequently, businesses may reduce their capital spending, resulting in a slowdown in economic growth.
2. Effect on Consumption
Rising interest rates can also influence consumer behavior. When borrowing becomes more expensive, individuals are less likely to take out loans for major purchases like homes, cars, or appliances. This decrease in consumer borrowing can lead to a decline in consumption as people have less access to credit. As a result, industries dependent on consumer spending, such as retail and housing, may experience a slowdown.
3. Impact on Savings and Investment Alternatives
Higher interest rates can incentivize individuals to save more. When interest rates rise, banks and other financial institutions offer higher returns on savings accounts and other investment products. This can encourage individuals to save and invest their money in safer options instead of spending it. Increased savings can also provide banks with more funds to lend to businesses for investment purposes, ultimately positively impacting the economy.
4. Government Policy and Central Bank Role
Interest rates are often influenced by central banks through monetary policy. Central banks raise interest rates to control inflation and stimulate saving. Conversely, during periods of economic downturns, central banks may lower interest rates to boost spending and investment. These actions aim to stabilize the economy and manage the effects of interest rates on investment and consumption.
Conclusion
The impact of interest rates on investment and consumption cannot be understated. Fluctuations in interest rates have a profound effect on businesses, consumers, and the overall economy. Understanding these effects helps policymakers, businesses, and individuals make informed decisions to navigate and adapt to changing economic conditions.
The Impact of Interest Rates on Savings and Borrowing Activities
Interest rates play a crucial role in shaping the behavior of individuals and businesses when it comes to savings and borrowing activities. Whether you are a lender, borrower, or an observer of the economy, understanding the impact of interest rates is essential in making informed financial decisions. In this article, we will explore how interest rates affect savings and borrowing activities and their wider implications on the economy.
1. Savings Rates and Return on Investments
One of the key ways interest rates influence savings activities is through the potential return on investments. Higher interest rates generally mean higher returns on savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), and other investment vehicles. This encourages individuals to save more, as their money can grow at a faster rate. On the other hand, lower interest rates might discourage saving, as the potential returns may not be as attractive.
2. Cost of Borrowing
Interest rates also impact borrowing activities by determining the cost of borrowing money. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper, making it more appealing for individuals and businesses to take out loans. This can stimulate economic growth, as businesses have easier access to funds for expansion, and individuals can afford to make large purchases such as homes or cars. Conversely, higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing, potentially leading to a decrease in borrowing activities.
3. Consumer Spending and Business Investments
Changes in interest rates can have a significant impact on consumer spending and business investments. When interest rates are low, people tend to have more disposable income due to reduced borrowing costs. This can lead to increased consumer spending, driving economic growth. For businesses, low interest rates can make it more financially viable to invest in new projects or expand existing ones, as the cost of borrowing is lower. Conversely, higher interest rates can dampen consumer spending and business investments due to increased borrowing costs.
4. Inflation and Central Bank Policies
Inflation and central bank policies also play a role in the impact of interest rates. Central banks often adjust interest rates to control inflation and stabilize the economy. When inflation is high, central banks may increase interest rates to discourage excessive borrowing and spending, aiming to curb inflationary pressures. Conversely, during periods of low inflation or economic downturns, central banks may opt to lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and spending and encourage economic growth.
Conclusion
Interest rates have a far-reaching impact on savings and borrowing activities, as well as on the overall economy. Whether it’s influencing the return on savings, the cost of borrowing, consumer spending, or business investments, interest rates shape financial decisions and can drive economic trends. By staying informed about interest rate trends and understanding their implications, individuals and businesses can make sound financial choices tailored to the prevailing economic climate.
Conclusion
The impact of interest rates on the economy is undeniable. Fluctuations in interest rates have far-reaching consequences that touch every aspect of the economy, from individual borrowers to large corporations. When interest rates are low, it stimulates borrowing and investment, leading to increased consumer spending and economic growth. On the other hand, high interest rates can slow down borrowing and investment, resulting in reduced consumer spending and economic contraction.
Furthermore, interest rates also influence inflation rates and exchange rates. When interest rates are low, it encourages borrowing and spending, which in turn can lead to higher inflation rates. Conversely, higher interest rates can help control inflation by making borrowing more expensive and reducing consumer spending. Similarly, fluctuations in interest rates affect exchange rates as investors seek higher returns in countries with higher interest rates, causing the value of the currency to appreciate or depreciate.

