Understanding Capital Gains: A Complete Guide
Capital gains are an essential part of investing and can have a significant impact on your financial portfolio. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting to dip your toes into the stock market, it’s crucial to have a solid understanding of how capital gains work. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the concept of capital gains, providing you with essential knowledge to make informed investment decisions.
What are Capital Gains?
Capital gains refer to the profits or gains one earns from the sale of a capital asset, such as stocks, real estate, or artwork. It represents the difference between the purchase price of the asset and its selling price. When an asset is sold at a higher price than its purchase price, the investor realizes a capital gain.
Types of Capital Gains
There are two main types of capital gains:
- Short-term capital gains: These are gains from assets held for one year or less before being sold. Short-term capital gains are usually subject to higher tax rates than long-term gains.
- Long-term capital gains: These are gains from assets held for more than one year before being sold. Long-term capital gains are typically eligible for lower tax rates, encouraging long-term investment strategies.
Capital Gains Tax
Capital gains are subject to taxation in many countries. The tax rate on capital gains depends on various factors such as the holding period, the type of asset, and the taxpayer’s income level. It is important for investors to understand their tax obligations related to capital gains.
Calculating Capital Gains
To calculate capital gains, subtract the purchase price (including any additional costs like commissions or fees) from the selling price. The resulting amount is the capital gain. However, it’s important to note that certain adjustments or deductions may apply depending on the tax jurisdiction.
Importance of Understanding Capital Gains
Understanding capital gains is crucial for investors as it affects their overall investment strategy, tax liabilities, and financial planning. By comprehending the concept of capital gains, investors can make informed decisions regarding buying, selling, or holding onto assets.
Types of Capital Gains
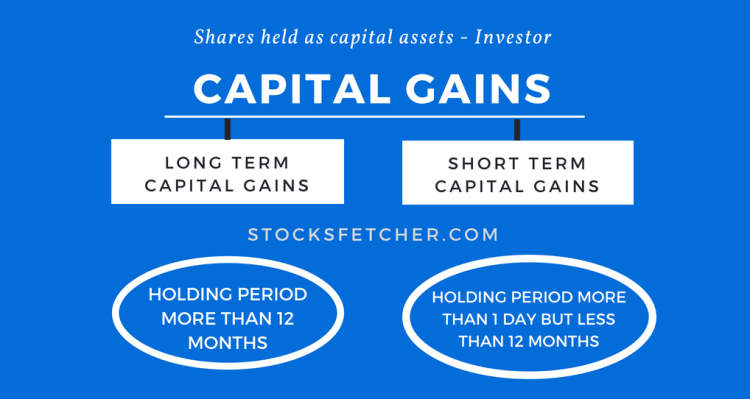
When it comes to understanding capital gains, it is essential to know that there are different types of capital gains that investors may encounter. These types can vary based on various factors, including the holding period and the type of asset being sold. Here are some of the common types of capital gains:
1. Short-Term Capital Gains
Short-term capital gains refer to profits made from the sale of assets held for less than one year. These gains are typically taxed at a higher rate compared to long-term capital gains.
2. Long-Term Capital Gains
Long-term capital gains occur when assets are sold after being held for more than one year. These gains are generally taxed at a lower rate, incentivizing long-term investments.
3. Collectibles Capital Gains
Collectibles, such as artwork, antiques, coins, or precious metals, may be subject to a different tax rate when sold. The gains from these collectibles are known as collectibles capital gains.
4. Real Estate Capital Gains
Real estate investments can also generate capital gains when the property is sold for a profit. These gains are referred to as real estate capital gains and may have specific tax regulations.
5. Stock and Mutual Fund Capital Gains
Stocks and mutual funds are common investment vehicles that can generate capital gains. When investors sell their shares or units at a profit, they realize stock and mutual fund capital gains.
6. Business Capital Gains
Business owners who sell their business assets or shares at a profit may generate business capital gains. These gains are subject to unique tax rules and regulations.
Understanding the different types of capital gains is crucial for investors to effectively plan their investment strategies and manage their tax liabilities. It is advisable to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor who can provide guidance based on individual circumstances.
Calculating and Reporting Capital Gains
Understanding how to calculate and report capital gains is essential for any investor. Whether you’re buying and selling stocks, real estate, or other assets, knowing the ins and outs of capital gains can significantly impact your financial success. In this guide, we will break down the key concepts and steps involved in calculating and reporting capital gains.
What are Capital Gains?
Capital gains refer to the profits made from the sale or disposition of a capital asset. These assets can include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate properties, and more. When you sell an asset for a higher price than what you initially paid for it, the difference is considered a capital gain.
How to Calculate Capital Gains
Calculating capital gains involves a simple formula:
Capital Gain = Selling Price – Cost Basis
The selling price is the amount you received from selling the asset, while the cost basis is the original purchase price plus any additional expenses, such as commissions or fees. Keep in mind that certain adjustments, such as depreciation for real estate, may also affect the cost basis.
Reporting Capital Gains
Reporting capital gains typically involves filing your annual tax return with the appropriate forms, such as Schedule D (Capital Gains and Losses). The tax treatment of capital gains can vary depending on factors like the holding period of the asset and your tax bracket.
- If you held the asset for less than a year before selling it, the gain is considered short-term and taxed at your ordinary income tax rate.
- For assets held for more than a year, the gain is classified as long-term, and the tax rate may be lower, subject to certain capital gains tax brackets.
It’s crucial to keep accurate records of all relevant transactions, including purchase and sale dates, prices, and associated expenses. This will help ensure accurate reporting and potentially minimize your tax liability.
Conclusion
Understanding how to calculate and report capital gains is essential for any investor aiming for financial success. By familiarizing yourself with the key concepts and steps involved, you can make informed decisions and optimize your tax strategies. Remember to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor for personalized advice based on your specific circumstances.
Conclusion
Understanding capital gains is essential for anyone looking to invest in assets such as stocks, real estate, or businesses. The concept of capital gains refers to the profit made from the sale of these assets, and it has significant implications for investors in terms of taxes and wealth accumulation.
By learning about capital gains, investors can make informed decisions regarding when to buy and sell assets to maximize their profits and minimize taxes. It is crucial to understand the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains, as the tax rates and holding periods vary. Additionally, various tax strategies, such as tax-loss harvesting or tax-deferred accounts, can help investors optimize their overall tax liabilities.

