The Impact of Mortgage Rates on Homebuyers: Everything You Need to Know
When it comes to purchasing a home, one of the most significant factors that homebuyers need to keep an eye on is mortgage rates. Mortgage rates play a crucial role in determining the total cost of homeownership and can have a substantial impact on the financial well-being of buyers. In this article, we will explore how mortgage rates affect homebuyers and provide you with everything you need to know to make informed decisions about your home purchase.
The Definition of Mortgage Rates
Mortgage rates refer to the interest rates that lenders charge borrowers for a mortgage loan. These rates determine the cost of borrowing money to finance the purchase of a home. Typically, mortgage rates are expressed as an annual percentage rate (APR) and can vary depending on a variety of factors, including the borrower’s credit score, the loan amount, and the term of the loan.
Understanding mortgage rates is crucial for potential homebuyers as they directly impact the overall affordability of a home and the monthly mortgage payments. Here is everything you need to know about mortgage rates:
1. Fixed-Rate Mortgages
A fixed-rate mortgage is a type of mortgage loan where the interest rate remains the same throughout the entire term of the loan. This means that the monthly mortgage payment will also remain constant. Fixed-rate mortgages provide stability and predictability, making them an attractive option for many homebuyers.
2. Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARM)
An adjustable-rate mortgage, commonly known as an ARM, is a type of mortgage loan where the interest rate can fluctuate over time. Typically, ARMs have a fixed rate for an initial period, after which the rate adjusts periodically based on an index such as the U.S. Treasury bill rate. ARMs offer lower initial rates compared to fixed-rate mortgages but carry the risk of potentially higher rates in the future.
3. Factors Affecting Mortgage Rates
Several factors influence mortgage rates. The primary factor is the broader economic conditions, including the state of the economy, inflation rate, and market trends. Additionally, the borrower’s credit score, debt-to-income ratio, and loan-to-value ratio also play a significant role in determining the mortgage rate offered by lenders.
4. Impact on Homebuyers
Mortgage rates directly impact homebuyers in several ways. Higher mortgage rates lead to increased monthly mortgage payments, which can reduce affordability and limit the purchasing power of potential buyers. Conversely, lower mortgage rates can make homes more affordable and lead to increased demand for home purchases.
It is important for homebuyers to monitor mortgage rates and understand how they can impact their financial situation when considering purchasing a home. By staying informed and working with knowledgeable professionals, homebuyers can make informed decisions and navigate the complex world of mortgage rates.
The Factors Affecting Mortgage Rates
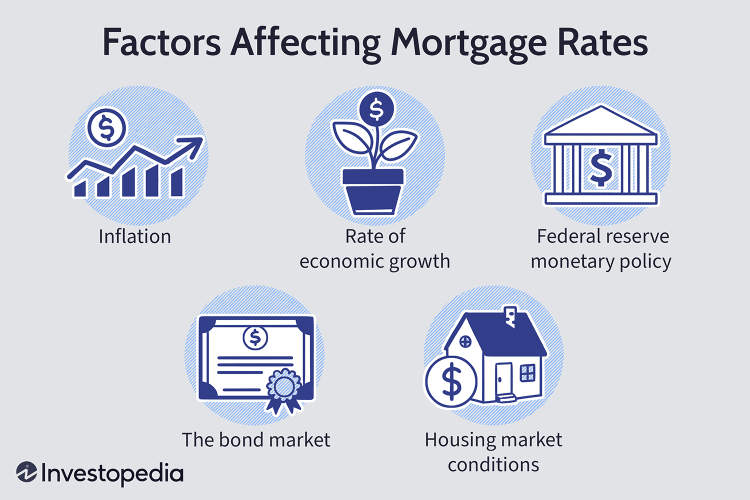
Mortgage rates play a crucial role in the homebuying process, as they determine the cost of borrowing for individuals looking to purchase a home. Various factors influence mortgage rates, impacting both the fixed and adjustable rate mortgages. Understanding these factors can help potential homebuyers make informed decisions when it comes to financing their dream home.
Economic Conditions
The overall health of the economy significantly affects mortgage rates. In times of economic growth and stability, mortgage rates tend to be higher due to increased demand. Conversely, during times of economic uncertainty or recession, mortgage rates tend to decrease as lenders try to stimulate borrowing and homeownership.
Inflation
Inflation is another key factor influencing mortgage rates. When inflation is high, lenders charge higher interest rates to compensate for the decrease in purchasing power over time. Conversely, when inflation is low, mortgage rates tend to be lower as lenders have less need to compensate for the eroding value of money.
Creditworthiness
Individuals’ creditworthiness is crucial in determining the mortgage rate they qualify for. Lenders assess factors such as credit score, debt-to-income ratio, and payment history to gauge an individual’s ability to repay the mortgage. Those with excellent credit scores and low debt ratios typically qualify for lower mortgage rates, while those with poor credit scores may face higher rates or difficulty securing a mortgage.
Loan Term
The length of the mortgage loan term also affects the interest rate. Generally, shorter-term loans have lower interest rates compared to longer-term loans. This is because lenders take on less risk with shorter-term loans as the repayment period is shorter.
Government Policies
Government actions, such as changes in monetary policy or housing regulations, can impact mortgage rates. For example, if the government implements policies to encourage homeownership or promote economic growth, it may lead to lower mortgage rates. Conversely, changes in regulations or financial market conditions may result in higher rates.
Market Competition
The level of competition among lenders also influences mortgage rates. When multiple lenders vie for borrowers’ business, they may offer lower rates and more favorable terms to attract customers. Conversely, if lenders have limited competition, they may have less incentive to offer competitive rates.
Down Payment and Loan Amount
The down payment amount and loan-to-value ratio can impact mortgage rates. Generally, individuals with larger down payments or lower loan-to-value ratios are perceived as lower risk by lenders, leading to lower rates. In contrast, individuals with smaller down payments or higher loan-to-value ratios may face higher interest rates.
Interest Rate Type
The type of interest rate chosen, whether fixed or adjustable, also affects the mortgage rate. Fixed-rate mortgages have stable interest rates throughout the loan term, while adjustable-rate mortgages have rates that can fluctuate. Generally, fixed-rate mortgages tend to have slightly higher rates compared to the initial rate of an adjustable-rate mortgage.
Understanding these factors can empower homebuyers to make informed decisions when it comes to securing the best mortgage rates for their financial situation. It is crucial for individuals to research and compare offers from different lenders to find the most favorable terms available.
The Effects of Mortgage Rates on Homebuyers
When it comes to buying a home, mortgage rates play a crucial role in determining affordability and overall financial impact. These rates, which are influenced by various economic factors, can have significant effects on homebuyers. Understanding these effects is essential for anyone considering homeownership. In this article, we will explore the impact of mortgage rates on homebuyers and provide you with everything you need to know.
1. Affordability
Mortgage rates directly affect how much homebuyers can afford to borrow. When rates are low, buyers can obtain larger loans without significantly increasing their monthly payments. On the other hand, when rates are high, the cost of borrowing increases, making it harder for buyers to qualify for loans and reducing their purchasing power.
2. Monthly Payments
Higher mortgage rates result in higher monthly payments for homebuyers. Even a small increase in rates can have a substantial impact on monthly expenses, especially with long-term mortgages. It’s important for buyers to carefully consider their budgets and factor in the potential fluctuations in mortgage rates to ensure they can comfortably manage their monthly payments.
3. Real Estate Market
Mortgage rates can influence the dynamics of the real estate market. When rates are low, more buyers can enter the market as home affordability increases. This high demand can lead to bidding wars and an increase in home prices. Conversely, when rates are high, the demand for homes tends to decrease, which could lead to a softening of prices and more negotiation power for buyers.
4. Refinancing Opportunities
Fluctuating mortgage rates also impact homeowners who may consider refinancing their mortgages. When rates drop significantly, homeowners can take advantage of refinancing to secure a lower interest rate and potentially reduce their monthly payments. However, when rates rise, the window for refinancing at a favorable rate may close, resulting in missed opportunities for homeowners to save money.
5. Long-term Financial Planning
Mortgage rates have long-term implications on homebuyers’ financial planning. Locked into a mortgage, homebuyers should consider the potential rise or fall of rates to ensure their long-term financial stability. Financial experts often recommend that buyers evaluate their options and determine the best time to purchase a home based on current and projected mortgage rate trends.
In conclusion, mortgage rates have a profound impact on homebuyers. From affordability and monthly payments to the real estate market and long-term financial planning, understanding the effects of mortgage rates is crucial for anyone considering buying a home. By staying informed about current rates and trends, homebuyers can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
Conclusion
The impact of mortgage rates on homebuyers is undeniable. As we have discussed in this article, mortgage rates play a crucial role in determining the affordability of a home purchase. When rates are low, homebuyers can take advantage of lower monthly payments and potentially secure a larger loan amount. On the other hand, when rates are high, homebuyers may face higher monthly payments and have to settle for a smaller loan.
Furthermore, mortgage rates also have the power to influence the housing market as a whole. Lower rates can stimulate demand, leading to an increase in home prices. Conversely, higher rates can dampen demand, causing home prices to stabilize or even decrease. As such, it is essential for both buyers and sellers to monitor mortgage rate trends and adjust their strategies accordingly.